Mangala Fossa
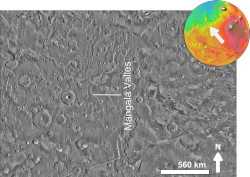
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars , located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W , which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs . The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles , which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons , resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick " cryosphere " (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7]
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
90524 characters 5 sections 6 paragraphs 7 images 666 internal links 14 external links |
mangala 0.660 graben 0.360 fossa 0.264 151 0.234 dike 0.159 valles 0.142 head 0.137 memnonia 0.124 overflowing 0.122 jyotish 0.110 subsided 0.094 spilled 0.091 beneath 0.089 emplacement 0.086 epochs 0.084 |
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars , located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W , which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs . The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles , which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons , resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick " cryosphere " (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] |
|
| 2017 |
48729 characters 5 sections 6 paragraphs 10 images 173 internal links 12 external links |
mangala 0.660 graben 0.360 fossa 0.264 151 0.234 dike 0.159 valles 0.142 head 0.137 memnonia 0.124 overflowing 0.122 jyotish 0.110 subsided 0.094 spilled 0.091 beneath 0.089 emplacement 0.086 epochs 0.084 |
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars , located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W , which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs . The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles , which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons , resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick " cryosphere " (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] |
|
| 2016 |
47038 characters 5 sections 6 paragraphs 10 images 171 internal links 11 external links |
mangala 0.660 graben 0.360 fossa 0.264 151 0.234 dike 0.159 valles 0.142 head 0.137 memnonia 0.124 overflowing 0.122 jyotish 0.110 subsided 0.094 spilled 0.091 beneath 0.089 emplacement 0.086 epochs 0.084 |
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars , located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W , which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs . The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles , which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons , resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick " cryosphere " (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] |
|
| 2015 |
47036 characters 5 sections 6 paragraphs 10 images 171 internal links 11 external links |
mangala 0.660 graben 0.360 fossa 0.264 151 0.234 dike 0.159 valles 0.142 head 0.137 memnonia 0.124 overflowing 0.122 jyotish 0.110 subsided 0.094 spilled 0.091 beneath 0.089 emplacement 0.086 epochs 0.084 |
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars , located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W , which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs . The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles , which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons , resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick " cryosphere " (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] |